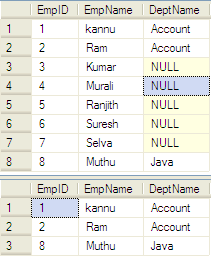
DECLARE @Employee TABLE ( EmpID INT, EmpName VARCHAR(50), DeptID INT ) INSERT INTO @Employee SELECT 1,'kannu',1 UNION ALL SELECT 2,'Ram',1 UNION ALL SELECT 3,'Kumar',2 UNION ALL SELECT 4,'Murali',3 UNION ALL SELECT 5,'Ranjith',4 UNION ALL SELECT 6,'Suresh',4 UNION ALL SELECT 7,'Selva',5 UNION ALL SELECT 8,'Muthu',6 DECLARE @Department TABLE ( DeptID INT, DeptName VARCHAR(50) ) INSERT INTO @Department SELECT 1,'Account' UNION ALL SELECT 2,'Testing' UNION ALL SELECT 3,'Web Develop' UNION ALL SELECT 5,'PDA Develop' UNION ALL SELECT 6,'Java' UNION ALL SELECT 7,'DBA'
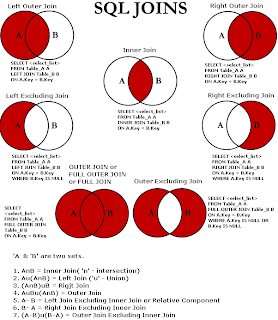
What is Join in SQL SERVER?
The JOIN keyword is used in an SQL statement to query data from two or more tables, based on a relationship between certain columns in these tables.
Join Types
- Inner Join
- Inner Join
- Equi-Join
- Natural Join
- Outer join
- Left Join
- Left Join Excluding Inner Join
- Right Join
- Right Join Excluding Inner Join
- Full Outer Join
- Outer Join Excluding Inner Join Or Left & Right Joins Excluding Inner Join
- Left Join
- Cross Join / Cartesian product
- Self Join / Auto Join
Join
The query compares each row of table(@Employee) with each row of table(@Department) to find all pairs of rows which satisfy the join predicate.
Inner Join
The query produces a new result set by combining the column values of both the table @Employee and @Department.
It will produce the resultset if there is atleast one match.
An inner join is a join with a join condition that may contain both equality and non-equality sign whereas an equijoin is a join with a join condition that only contain only equality sign. So we can say an equijoin is a type of inner join containing (Equal)= operator in the join condition.
It is good to know the difference between join and INNER JOIN keyword. Actually there is no difference. If we write JOIN then by default INNER JOIN is performed.
Equi-join or Inner Join
Join based on equality test. Using other operator disqualifies equijoin.
SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
INNER JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
Complex Join Or Inner Join If join nested then it is called complex join
Jon based on more then one column from each table.
Natural Join
Select the Particular column in Both TableA and TableB. Both table should have same no of columns and names (i.e. Identical columns in both tables). This is accomplished by using union operator in both the select statement.
SELECT EmpID ,
EmpName,
DeptID
FROM @Employee
UNION --Eliminates duplicates
--UNION ALL --Get all the records from both the table
SELECT EmpID ,
EmpName,
DeptID
FROM @Employee
Outer JoinLeft Outer Join
Display all columns in left side and only Match values in right side. Remaining values will be NULL.
SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
LEFT OUTER JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
Left Join Excluding Inner Join SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
LEFT JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
WHERE B.DeptID IS NULL
Difference between On clause and Where clause when used with left join SELECT E.EmpID ,
E.EmpName,
D.DeptName
FROM @Employee AS E
LEFT JOIN @Department AS D
ON D.DeptID = E.DeptID
AND
(
D.DeptName = 'Account'
OR D.DeptName = 'Java'
)
SELECT E.EmpID ,
E.EmpName,
D.DeptName
FROM @Employee AS E
LEFT JOIN @Department AS D
ON D.DeptID = E.DeptID
WHERE (
D.DeptName = 'Account'
OR D.DeptName = 'Java'
)
Now let us understand ON clause it is apply before JOIN that is why it retrieves all the result of Table2 where there are Flag = 1 but it does not affect Table1 so it retrieves all the rows of table1. When WHERE clause is applied it applies to complete result so it removes all the rows from Table1 and Table2 where Flag is not equal to 1, essentially keeping flag = 1 rows from Table1 and Table2. Right Outer Join
Just Opposite Of Left Outer Join
SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
RIGHT JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
Right Join Excluding Inner Join
SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
RIGHT JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
WHERE A.DeptID IS NULL
Full Outer Join A full outer join combines the results of both left and right outer joins. The joined table will contain all records from both tables, and fill in NULLs for missing matches on either side.
SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
FULL OUTER JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
Outer Join Excluding Inner Join Or Left & Right Joins Excluding Inner Join SELECT A.EmpID ,
A.EmpName,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID ,
B.DeptName
FROM @Employee A
FULL OUTER JOIN @Department B
ON A.DeptID=B.DeptID
WHERE A.DeptID IS NULL
OR B.DeptID IS NULL
Cartesian Product Or Cross Join Known as Join without condition
ResultSet = No of Rows in TableA * No of Rows in TableB
Display all the Possibilities of combinations.
SELECT * FROM @Employee INNER JOIN @Department ON 1 = 1 --Explicit SELECT * FROM @Employee CROSS JOIN @Department --Implicit SELECT * FROM @Employee, @DepartmentSelf-Join
A table joins with itself with one or two aliases to stave off confusion are called self-join.
SELECT A.EmpName ,
B.EmpName ,
A.DeptID ,
B.DeptID
FROM @Employee A
INNER JOIN @Employee B
ON A.DeptID = B.DeptID
References:
codeproject
wikipedia
c-sharpcorner.com
techbubbles
marcoullis
Logical Query Processing